Publikationen
-
Metaverse in Civil Engineering
N. Bartels, A. Fuhrmann, R. Kasper, P. Di Biase, K. Hahne: Metaverse in Civil Engineering
In: 4th IEEE German Education Conference (GECon), 2025 -
Investigating the Impact of Video Pass-Through Embodiment on Presence and Performance in Virtual Reality
Kristoffer Waldow, Constantin Kleinbeck, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Daniel Roth
In: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2025)
🏆Honorable Mention Best Paper Award -
DimSplat: A Real-Time Diminished Reality System for Revisiting Environments Using Gaussian Splats in Mobile WebXR
Kristoffer Waldow, Jonas Scholz, Arnulph Fuhrmann
In: Proceedings of 32th IEEE Virtual Reality Conference (VR ’25), Saint-Malo, France -
3D Gaussian Splatting for Construction Sites
Sina Rüter, Kristoffer Waldow, Niels Bartels and Arnulph Fuhrmann
Conference: 24th International Conference on Construction Applications of Virtual Reality (CONVR 2024),Western Sydney University, NSW, Australia -
Rendering diffraction Phenomena on rough surfaces in Virtual Reality
Olaf Clausen, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Martin Mišiak, Marc Erich Latoschik and Ricardo Marroquim
VRST ’24: Proceedings of the 30th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology -
Anti-aliasing Techniques in Virtual Reality: A User Study with Perceptual Pairwise Comparison Ranking Scheme
Waldow, Kristoffer; Scholz, Jonas; Misiak, Martin; Fuhrmann, Arnulph; Roth, Daniel; Latoschik and Marc Erich Latoshik
Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realität – 21. Workshop der GI-Fachgruppe VR/AR, 2024, , Germany -
Importance of multi-modal data for predictive rendering
Olaf Clausen, Y Chen, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Ricardo Marroquim
MANER Conference – Material Appearance Network for Education and Research (2024), Workshop on Material Appearance Modeling -
A Practical Real-Time Model for Diffraction on Rough Surfaces
Olaf Clausen, Martin Mišiak, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Ricardo Marroquim and Marc Erich Latoschik
Journal of Computer Graphics Techniques (JCGT), vol. 13, no. 1, 1-27, 2024 -
Facial Feature Enhancement for Immersive Real-Time Avatar-Based Sign Language Communication using Personalized CNNs
Kristoffer Waldow, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Daniel Roth
Proceedings of 31th IEEE Virtual Reality Conference (VR ’24), Orlando, USA -
Investigating Incoherent Depth Perception Features in Virtual Reality using Stereoscopic Impostor-Based Rendering
Kristoffer Waldow, Lukas Decker, Martin Misiak, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Daniel Roth, Marc Erich Latoschik
In:Proceedings of 31th IEEE Virtual Reality Conference (VR ’24), Orlando, USA
🏆Best Poster Award -
Deep Neural Labeling: Hybrid Hand Pose Estimation Using Unlabeled Motion Capture Data With Color Gloves in Context of German Sign Language
Kristoffer Waldow, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Daniel Roth
6th IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence & extended and Virtual Reality 2024 (AIxVR ’24) -
An Evaluation of Dichoptic Tonemapping in Virtual Reality Experiences
Martin Mišiak, Tom Müller, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Marc Erich Latoschik
Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realität – 20. Workshop der GI-Fachgruppe VR/AR, 2023, Köln, Germany -
The Impact of Reflection Approximations on Visual Quality in Virtual Reality
Martin Mišiak, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Marc Erich Latoschik
ACM Symposium on Applied Perception 2023 (SAP ’23) -
Investigation and Simulation of Diffraction on Rough Surfaces
Olaf Clausen, Yang Chen, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Ricardo Marroquim
Computer Graphics Forum, 42: 245-260. -
Impostor-based Rendering Acceleration for Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Reality
Martin Mišiak, Arnulph Fuhrmann, Marc Erich Latoschik
Proceedings of the 27th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology. 2021 -
Investigating the Influence of Sound Source Visualization on the Ventriloquism Effect in an Auralized Virtual Reality Environment
Nigel Frangenberg, Kristoffer Waldow and Arnulph Fuhrmann
Proceedings of 28th IEEE Virtual Reality Conference (VR ’21), Lisbon, Portugal -
Intersection-free mesh decimation for high resolution cloth models
Ursula Derichs, Martin Mišiak and Arnulph Fuhrmann
Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realität – 17. Workshop der GI-Fachgruppe VR/AR, 2020, Trier, Germany -
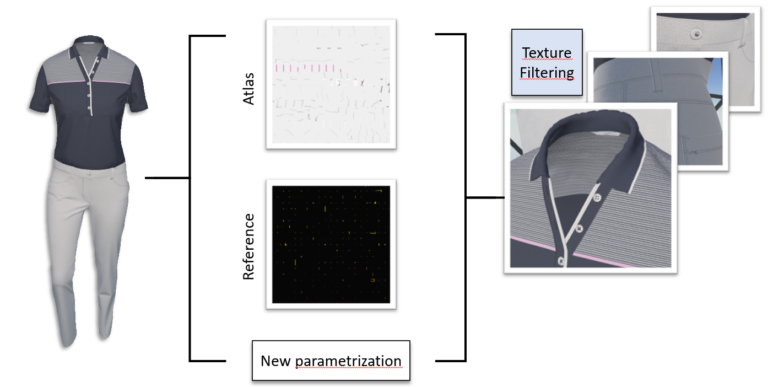
An Atlas-Packing Algorithm for Efficient Rendering of Arbitrarily Parametrized Decal Textures
Sven Hinze, Martin Mišiak and Arnulph Fuhrmann
Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realität – 17. Workshop der GI-Fachgruppe VR/AR, 2020, Trier, Germany -
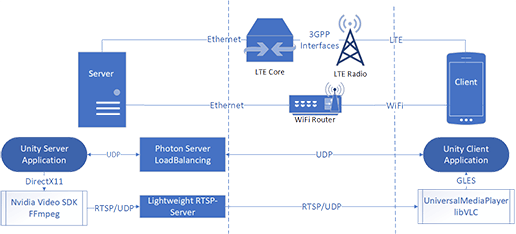
Performance of Augmented Reality Remote Rendering via Mobile Network
In this paper, a remote rendering system for an AR app based on Unity is presented. The system was implemented for an edge server, which is located within the network of the mobile network operator.
-
-
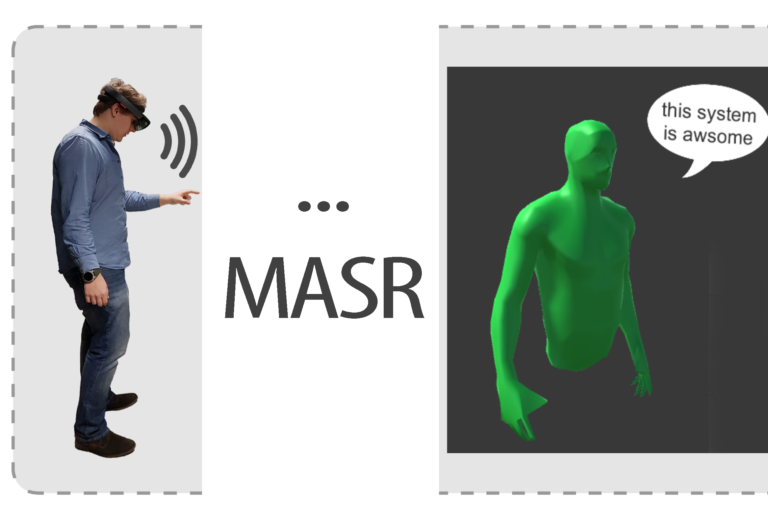
Addressing Deaf or Hard-of-Hearing People in Avatar-Based Mixed Reality Collaboration Systems
We propose an easy to integrate Automatic Speech Recognition and textual visualization extension for an avatar-based MR remote collaboration system that visualizes speech via spatial floating speech bubbles. In a small pilot study, we achieved word accuracy of our extension of 97% by measuring the widely used word error rate.
-
The Impact of Stereo Rendering on the Perception of Normal Mapped Geometry in Virtual Reality
This paper investigates the effects of normal mapping on the perception of geometric depth between stereoscopic and non-stereoscopic views.
-
Investigating the Effect of Embodied Visualization in Remote Collaborative Augmented Reality
Kristoffer Waldow, Arnulph Fuhrmann and Stefan M. Grünvogel In: Proceedings…
-
The influence of different audio representations on linear visually induced self-motion
We investigate the influence of four different audio representations on visually induced self-motion (vection). Our study followed the hypothesis, that the feeling of visually induced vection can be increased by audio sources while lowering negative feelings such as visually induced motion sickness.
-
-
Perceptual Comparison of Four Upscaling Algorithms for Low-Resolution Rendering for Head-mounted VR Displays
When rendering images in real-time, shading pixels is a comparatively expensive
operation. Especially for head-mounted displays, where separate images are rendered for
each eye and high frame rates need to be achieved. Upscaling algorithms are one possibility
of reducing the pixel shading costs. Four basic upscaling algorithms are implemented in a
VR rendering system, with a subsequent user study on subjective image quality. We find
that users preferred methods with a better contrast preservation. -
Using MQTT for Platform Independent RemoteMixed Reality Collaboration
In this paper, we present a Mixed Reality telepresence system that allows the connection of multiple AR or VR devices to create a shared virtual environment by using the simple MQTT networking protocol. It follows a subscribe-publish pattern for reliable and easy platform independent integration. Therefore, it is possible to realize different clients that handle communication and allow remote collaboration. To allow embodied natural human interaction, the system maps the human interaction channels, gestures, gaze and speech, to an abstract stylized avatar by using an upper body inverse kinematic approach. This setup allows spatially separated persons to interact with each other via an avatar-mediated communication.
-
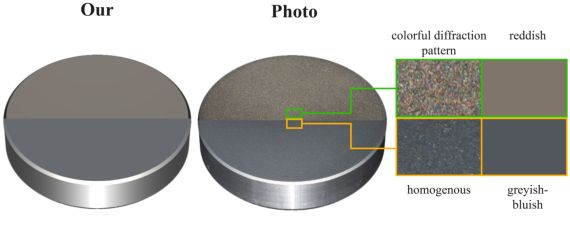
What is the Reddening Effect and does it really exist?
The simulation of light-matter interaction is a major challenge in computer graphics. Particularly challenging is the modelling of light-matter interaction of rough surfaces, which contain several different scales of roughness where many different scattering phenomena take place. There are still appearance critical phenomena that are weakly approximated or even not included at all by current BRDF models. One of these phenomena is the reddening effect, which describes a tilting of the reflectance spectra towards long wavelengths especially in the specular reflection. The observation that the reddening effect takes place on rough surfaces is new and the characteristics and source of the reddening effect have not been thoroughly researched and explained. Furthermore, it was not even clear whether the reddening really exists or the observed effect resulted from measurement errors. In this work we give a short introduction to the reddening effect and show that it is indeed a property of the material reflectance function, and does not originate from measurement errors or optical aberrations.
-
torVRt – Entwicklung eines Torwarttrainings zur Schulung von Antizipation und Reaktion in virtueller Realität
Um die Attraktivität des Antizipations- und Reaktionstrainings für jugendliche Torwarte zu erhöhen war es das Ziel eine sportartspezifische Umgebung in virtueller Realität (VR) zu entwickeln.
-
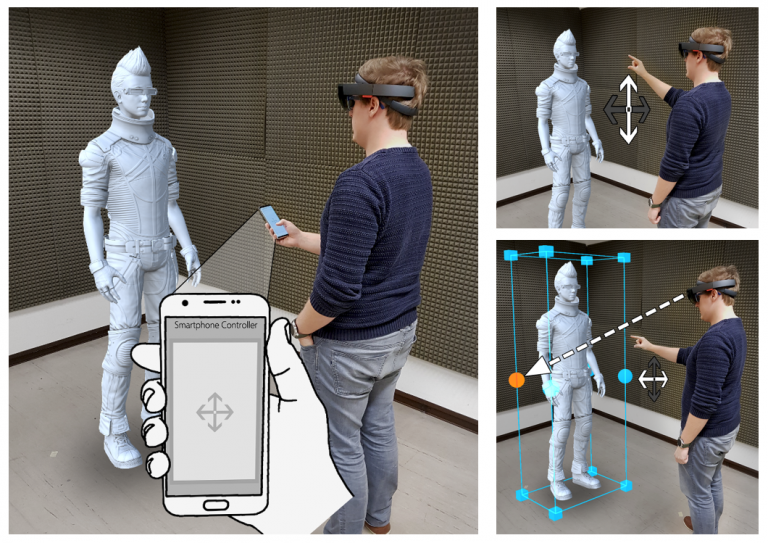
An Evaluation of Smartphone-Based Interaction in AR for Constrained Object Manipulation
In Augmented Reality, interaction with the environment can be achieved with a number of different approaches. In current systems, the most common are hand and gesture inputs. However experimental applications also integrated smartphones as intuitive interaction devices and demonstrated great potential for different tasks. One particular task is constrained object manipulation, for which we conducted a user study. In it we compared standard gesture-based approaches with a touch-based interaction via smartphone. We found that a touch-based interface is significantly more efficient, although gestures are being subjectively more accepted. From these results we draw conclusions on how smartphones can be used to realize modern interfaces in AR.
-
Localization Service Using Sparse Visual Information Based on Recent Augmented Reality Platforms
The ability to localize a device or user precisely within a known space, would allow many use cases on the context of location-based augmented reality. We propose a localization service based on sparse visual information using ARCore, a state-of-the-art augmented reality platform for mobile devices.
-
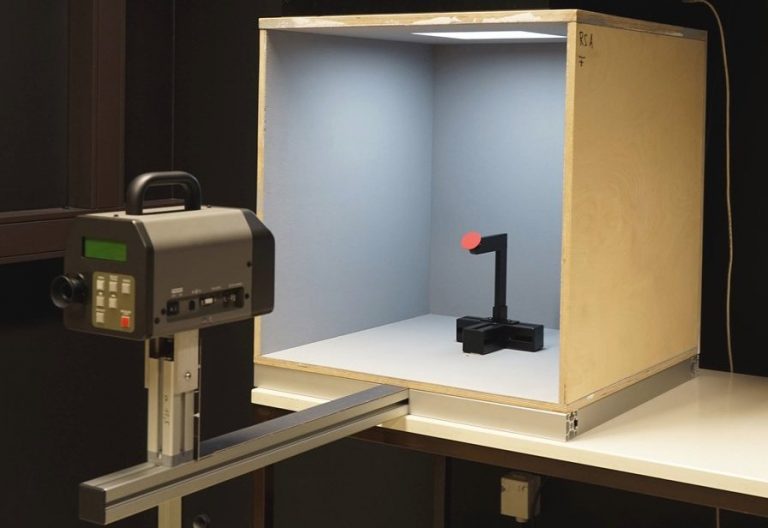
Acquisition and Validation of Spectral Ground Truth Data for Predictive Rendering of Rough Surfaces
In this work, we acquired a set of precisely and spectrally resolved ground truth data. It consists of the precise description of a new developed reference scene including isotropic BRDFs of 24 color patches, as well as the reference measurements of all patches under 13 different angles inside the reference scene.
-
Do Textures and Global Illumination Influence the Perception of Redirected Walking Based on Translational Gain?
For locomotion in virtual environments (VE) the method of redirected walking (RDW) enables users to explore large virtual areas within a restricted physical space by (almost) natural walking. The trick behind this method is to manipulate the virtual camera in an user-undetectable manner that leads to a change of his movements. If the virtual camera is manipulated too strong then the user recognizes this manipulation and reacts accordingly. We studied the effect of human perception of RDW under the influence of the level of realism in rendering the virtual scene.
-
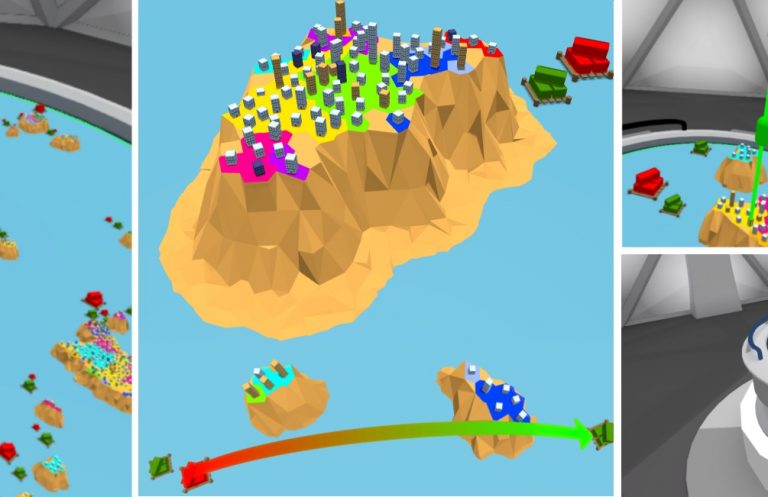
Immersive Exploration of OSGi-based Software Systems in Virtual Reality
We present an approach for exploring OSGi-based software systems in virtual reality. We employ an island metaphor, which represents every module as a distinct island. The resulting island system is displayed in the confines of a virtual table, where users can explore the software visualization on multiple levels of granularity by performing intuitive navigational tasks. Our approach allows users to get a first overview about the complexity of an OSGi-based software system by interactively exploring its modules as well as the dependencies between them.
-
Directional Occlusion via Multi-Irradiance Mapping
We present a new, physically plausible, real-time approach to compute directional occlusion for dynamic objects, lit with image based
lighting. -
Socially Immersive Avatar-Based Communication
In this paper, we present SIAM-C, an avatar-mediated communication platform to study socially immersive interaction in virtual environments.
-
The Effectiveness of Changing the Field of View in a HMD on the Perceived Self-Motion
The following paper investigates the effect on the intensity of perceived vection by changing the field of view (FOV) using a headmounted
display (HMD) in a virtual environment (VE). -
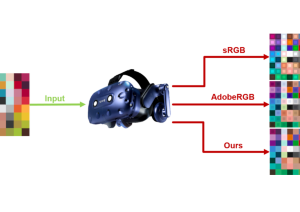
Real-time tone mapping – An evaluation of color-accurate methods for luminance compression
Recent advances in real-time rendering enable virtual production pipelines in a broad range of industries. These pipelines are based on a fast, latency-free handling in addition to the accurate appearance of results. This requires the use of high dynamic range rendering for photo-realistic results and a tone mapping operator for a matched display.
-
-
Avatar Realism and Social Interaction Quality in Virtual Reality
We describe an experimental method to investigate the effects of reduced social information and behavioral channels in immersive virtual environments with full-body avatar embodiment.
-
SVEn – Shared Virtual Environment
This paper presents a system for a shared virtual experience which was developed within a student project. The main idea is to have two or more persons at different locations, who can interact with each other in the same virtual environment. In order to realize this idea every person is motion-captured and wears a head-mounted display (HMD). The virtual environment is rendered with the Unity game engine and the tracked positions are updated via the internet. The virtual environment developed in this project is highly immersive and users felt a strong sense of presence.
-
Interaktive 3D Visualisierung
Inzwischen ermöglichen neue Algorithmen und hoch entwickelte GPUs das Rendering mit physikalisch basierten Modellen, wodurch die Darstellungsqualität realistisch geworden ist. Gleichzeitig kann die Geometrie mittels Echtzeitsimulation dynamisch verformt werden, so dass der Anwender sich nicht nur in der 3D Szene interaktiv bewegen, sondern diese auch sofort verändern kann.
-
Towards a Coupled Simulation of Cloth and Soft Tissue
In this paper, we present a possible guideline towards a coupled simulation of textiles and human soft tissue. We have developed a new simulator for soft tissue which is able to simulate the skin of a virtual human in a realistic manner.
-
Optimized Continuous Collision Detection for Deformable Triangle Meshes
We present different approaches for accelerating the process of continuous collision detection for deformable triangle meshes.
-
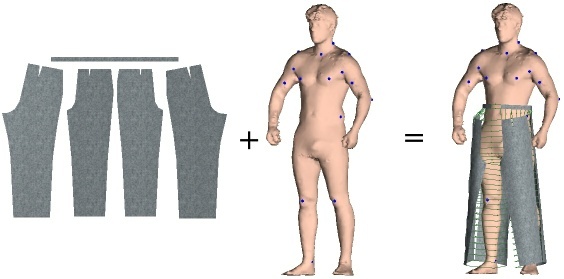
Ontologies for Virtual Garments
We give an ontology for garment patterns that can be incorporated into the simulation of virtual clothing. On the basis of this ontology and extensions to garments we can specify and manipulate the process of virtual dressing on a higher semantic level.
-
Real-Time Collision Detection for Dynamic Virtual Environments
Collision detection is an enabling technology for many virtual environments, games, and virtual prototyping applications containing some kind of physically-based simulation (such as rigid bodies, cloth, surgery, etc.). This tutorial will give an overview of the different classes of algorithms, and then provide attendees with in-depth knowledge of some of the important algorithms within each class.
-
Collision Detection for Deformable Objects
This paper summarizes recent research in the area of deformable collision detection. Various approaches based on bounding volume hierarchies, distance fields, and spatial partitioning are discussed. Further, image-space techniques and stochastic methods are considered.
-
Self-Shadowing of dynamic scenes with environment maps using the GPU
In this paper we present a method for illuminating a dynamic scene with a high dynamic range environment map with real-time or interactive frame rates, taking into account self shadowing. Current techniques require static geometry, are limited to few and small area lights or are limited in the frequency of the shadows.
-
Distance Fields for Rapid Collision Detection in Physically Based Modeling
In this paper we address the problem of rapid distance computation between rigid objects and highly deformable objects, which is important in the context of physically based modeling of e.g hair or clothing.
-
Interactive Animation of Cloth including Self Collision Detection
We describe a system for interactive animation of cloth, which can be used in e-commerce applications, games or even in virtual prototyping systems.
-
Interaction Free Dressing of Virtual Humans
🏆 Computers & Graphics best paper award (2003)